112. 路径总和
难度简单 523
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum ,判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
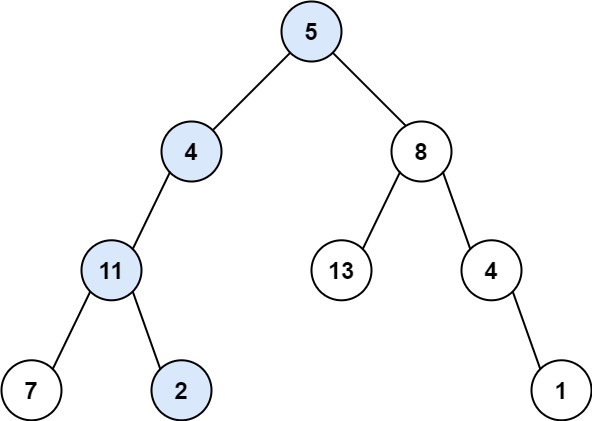
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22
输出:true
广度优先
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queNode = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<Integer> queVal = new LinkedList<Integer>();
queNode.offer(root);
queVal.offer(root.val);
while (!queNode.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode now = queNode.poll();
int temp = queVal.poll();
if (now.left == null && now.right == null) {
if (temp == sum) {
return true;
}
continue;
}
if (now.left != null) {
queNode.offer(now.left);
queVal.offer(now.left.val + temp);
}
if (now.right != null) {
queNode.offer(now.right);
queVal.offer(now.right.val + temp);
}
}
return false;
}
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-sum/solution/lu-jing-zong-he-by-leetcode-solution/递归
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return sum == root.val;
}
return hasPathSum(root.left, sum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, sum - root.val);
}
// 作者:LeetCode-Solution
// 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-sum/solution/lu-jing-zong-he-by-leetcode-solution/
}


